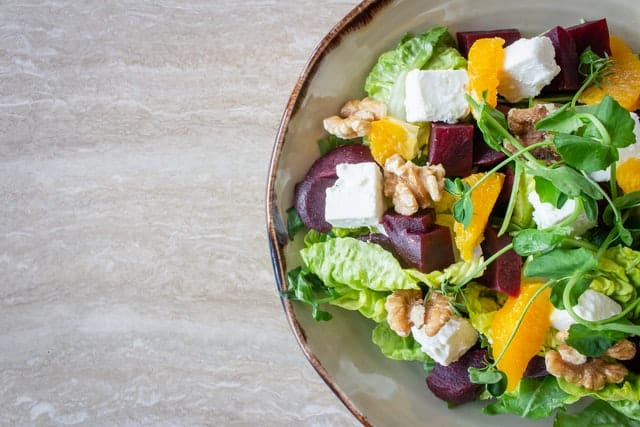
Low FODMAP Vegetables
Low FODMAP vegetables may trigger less digestive discomfort for those with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) because they’re easier to break down. If you are one of seven people living with IBS, you may have heard of the Low FODMAP diet. This science-based, digestion diet developed at Monash University in Australia, helps relieve symptoms of bloating, pain, gas and changes in bowels (i.e. diarrhea or constipation).
Importantly, working with a trained dietitian is key when navigating the Low FODMAP diet since it can be quite challenging. In today’s blog, we will ‘cut’ right into Low FODMAP vegetables, which ones are considered ‘safe’ and what you need to know to ease your digestive woes.
DYK: More than 20 million Canadians suffer from general digestive disorders every year (Can. Digestive Foundation, 2018) Share on XWhat are FODMAPs?
The acronym for FODMAP describes a collection of short-chain, poorly digested sugars. For those with digestive issues, these (poorly digested) sugars can trigger symptoms of abdominal pain, bloating and changes in bowel movements when broken down (or fermented) by colon bacteria. FODMAPs cause the bowel to distend by drawing more fluid (can cause diarrhea) and generating more gas by gut bacteria fermentation. Therefore, the main principle of the Low FODMAP diet is to replace sugars that are high in FODMAPs (a.k.a., small, poorly digested sugars) with sugars that are Low in FODMAPs (easily break down in the stomach).

Specifically for this blog, we are replacing High FODMAP vegetables with Low FODMAP vegetables. This relieves digestive distress and decreases the fermentation of hard-to-digest sugars in the colon, which can trigger uncomfortable symptoms. Interestingly, research shows that 3 out of 4 people find tremendous relief on this diet (The Complete Low-FODMAP Diet, 2013). Additionally, adopting a Low FODMAP diet helps people with IBS manage their condition without medication.

Determining FODMAPs in Vegetables?
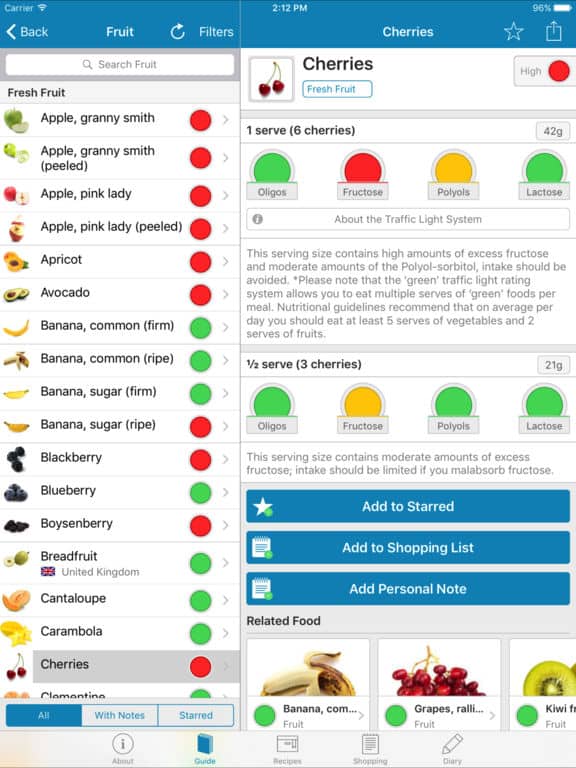
Monash University in Australia are pioneers in FODMAP research and testing. Their food lab tests foods and products to determine the safe or “green-light” serving size. Consequently, in Monash Low FODMAP app, you can search foods for Low FODMAP content. They use a traffic light system. Green is Low FODMAP, yellow is moderate (still safe during elimination phase), and red lights are high in FODMAPS.
What are Low FODMAP Vegetables?
- Carrots
- Bean Sprouts
- Eggplant
- Kale, Spinach, Arugula, Collard Greens, Radicchio
- Tomato
- Bell Peppers (green bell pepper has slightly higher sorbitol)
- Zucchini
- Cucumber
- Fresh Herbs (basil, parsley, chives, cilantro, mint, greens of scallions (LINK), etc)
- Beets (canned or pickled)
- Green or Red Cabbage (3/4 cup)
- Corn (1/2 cob)
- Fennel Bulb (few slices)
- White Potato
- Sweet potato (1/2 small)
- Canned Pumpkin
- Radish
- Green Beans
- Bok Choy (watch servings at 1 ¾ cup as considered high FODMAP)
- Broccoli (¾ cup of heads or ⅓ cup of stalks)
- Olives
- Canned Peas (1/3 cup)
- Spaghetti or Butternut Squash, ½ cup
- Parsnip
- Canned Mushrooms (6 mushrooms)
- Ginger Root
- Brussels Sprouts (4 sprouts)
- Asparagus (5 spears)
- Cauliflower (¾ cup serving)
- Leek bulb (½ cup)
- Button Mushrooms (½ cup)
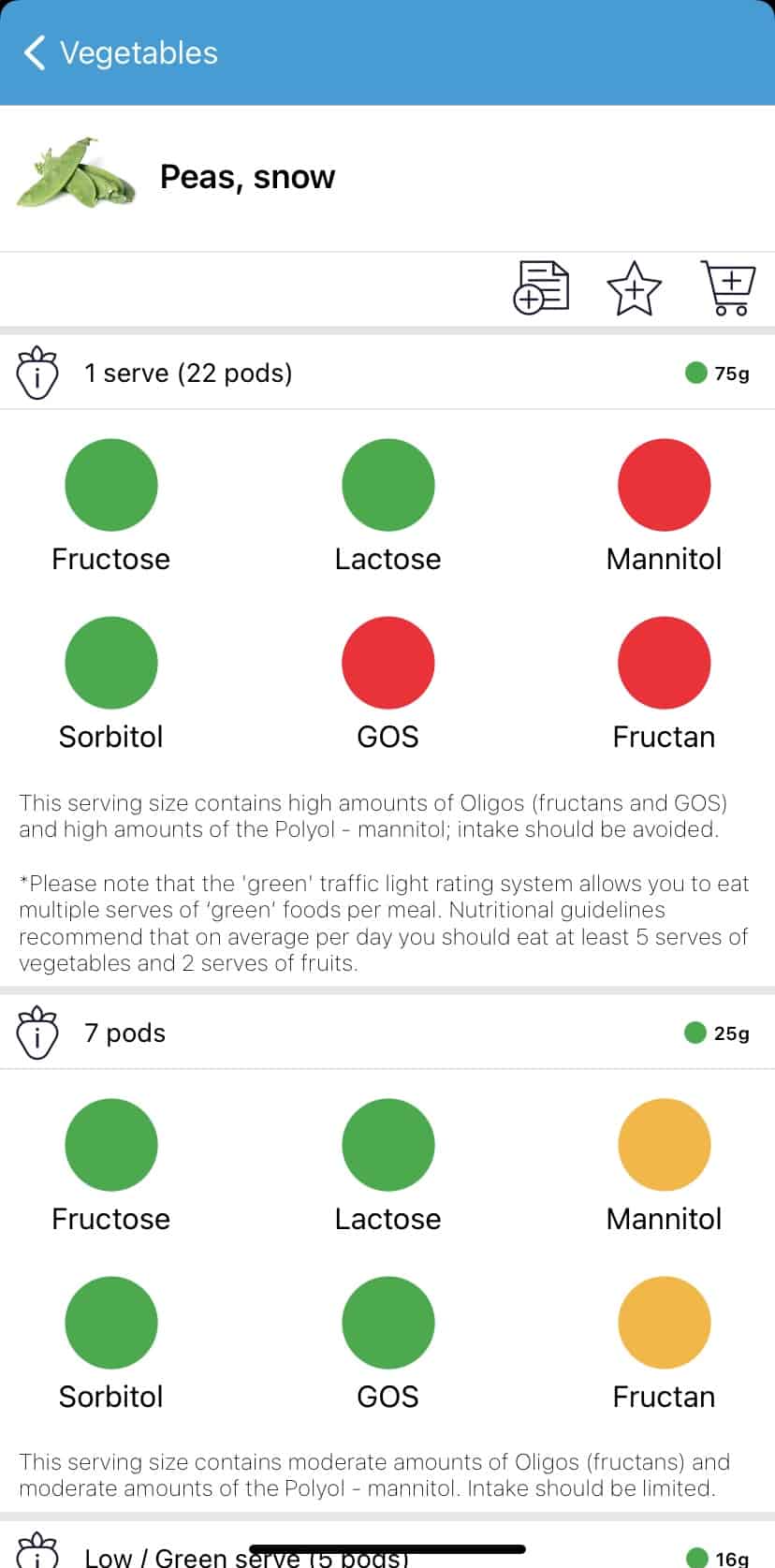
- Snow Peas, (22 pods)
- Fresh beets (1 small or ½ large)
CAUTION: This Low FODMAP vegetable list is not exhaustive. It’s best to check the Monash App for portion sizes and latest updates as they test new foods regularly.
Curious about Low FODMAP Vegetables? Here's what you need to know! #Dietitian #Digestion #FODMAPs Share on XWhy Are Many Canned Vegetables Low FODMAP?
You likely noticed from the above list that canned alternatives may be Low FODMAP. For example, mushrooms, peas, pumpkin, beets, etc. This is because the FODMAP sugars are water-soluble and can leach into the brining liquid. Consequently, this lowers the overall FODMAP level of canned foods. However, it’s still important to ensure a Low FODMAP portion size. Additionally, be sure to rinse the brine liquid of your canned vegetable (or small portion of canned beans/lentils) before consuming.
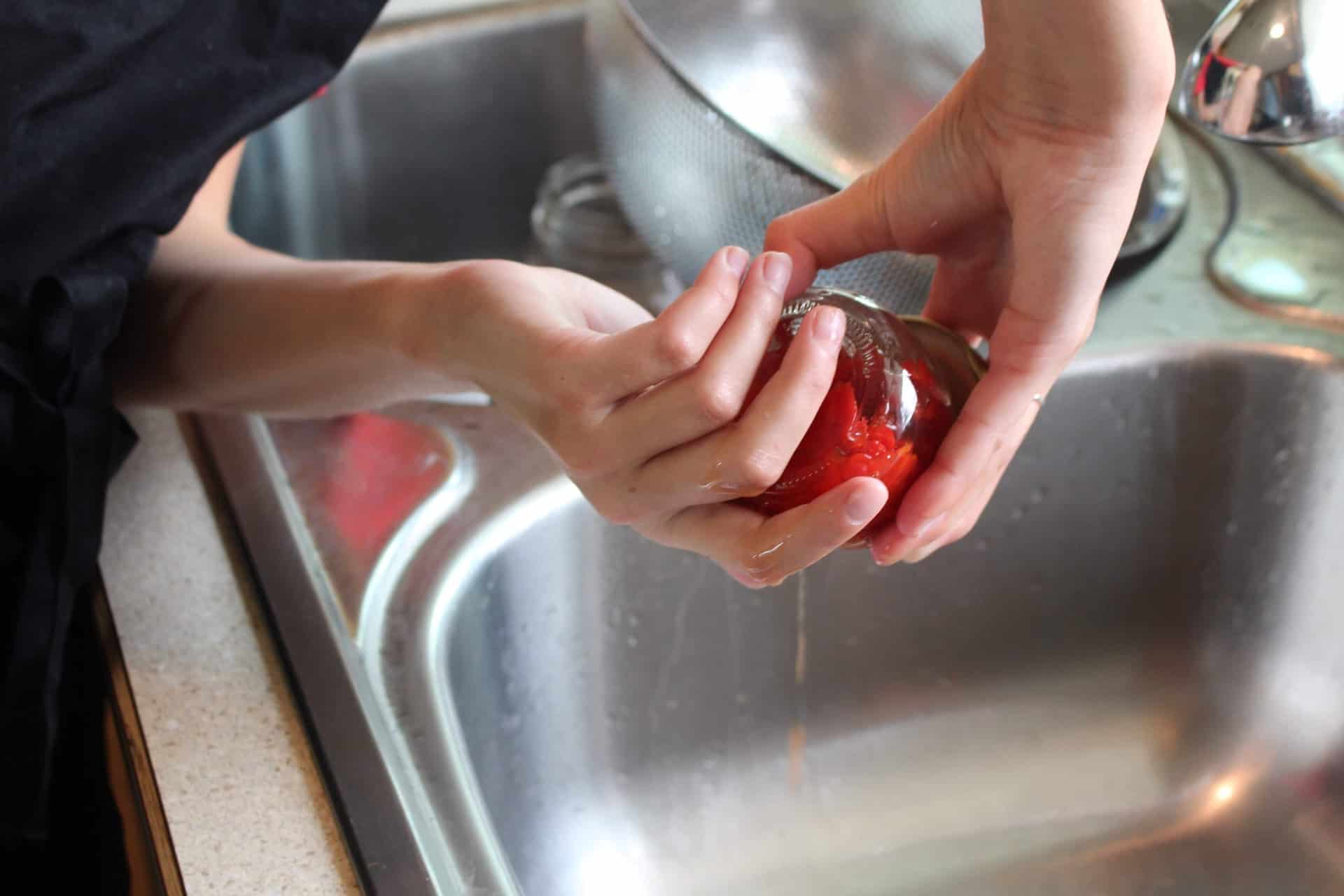

Interested in learning more about the nutritional value of canned vegetables? Check out our blog about canned vegetables vs. fresh vegetables.
Swap out Low FODMAP Vegetables!
Importantly, vegetables are part of a healthy diet and those with IBS don’t need to avoid them. Instead, if following the Low FODMAP Diet (ideally with a trained dietitian) we begin by replacing all High FODMAP foods with Low FODMAP alternatives. Therefore, in Phase 1 or the ‘Elimination Phase,’ the greens of scallions or garlic-infused oil (Low FODMAP vegetables)can substitute such High FODMAP vegetables as onions or garlic. Additionally, button mushrooms are High in FODMAPs at ½ cup (the mannitol sugar) but eggplant would be a low FODMAP vegetable alternative.
Dietitian Tip: Remember that Low FODMAPs Vegetables are not intuitive. However, it’s key to confidently reference amounts that are safe to consume.
Additionally, changing the serving size of your High FODMAP vegetables can make them Low FODMAP. For example, 22 snow pea pods is High FODMAP, whereas 7 pods is considered a Low FODMAP vegetable. For more information on the three phases of the Low FODMAP Diet, read our past blog Beat the Bloat with FODMAPs.
Low FODMAP Vegetables: Why so Complicated?
Low FODMAP Vegetables can be complex because they contain one of the most diverse ranges of FODMAP sugars. For example, fructans and mannitol are the main FODMAPs but there are often also galactooligosaccharides (GOS), fructose and sorbitol. Furthermore, several vegetables contain more than one type of FODMAP sugar. For example, 5 asparagus spears contain fructans and fructose. Keep in mind, you don’t need to memorize these sugars. Instead, you can look foods up on an app for FODMAPs.

Is the Low FODMAP Diet Long-Term?
Importantly, the FODMAP Diet goes through different phases, from the elimination phase to reintroduction and finally, personalization. You can read about the Low FODMAP diet phases in more detail here. The strict Low FODMAP diet is NOT long-term. Therefore, it is vital to remove high FODMAP foods during the elimination phase only. Ideally, your dietitian is assisting you with reintroductions as well.
Finally, after your digestive symptoms have subsided and you have done your FODMAP challenges, you will have a clear idea of tolerance to specific FODMAP sugars. This will allow you to determine which vegetables you can bring back into your diet without digestive discomfort. Your dietitian will be very helpful during this challenging and re-integrating stage!
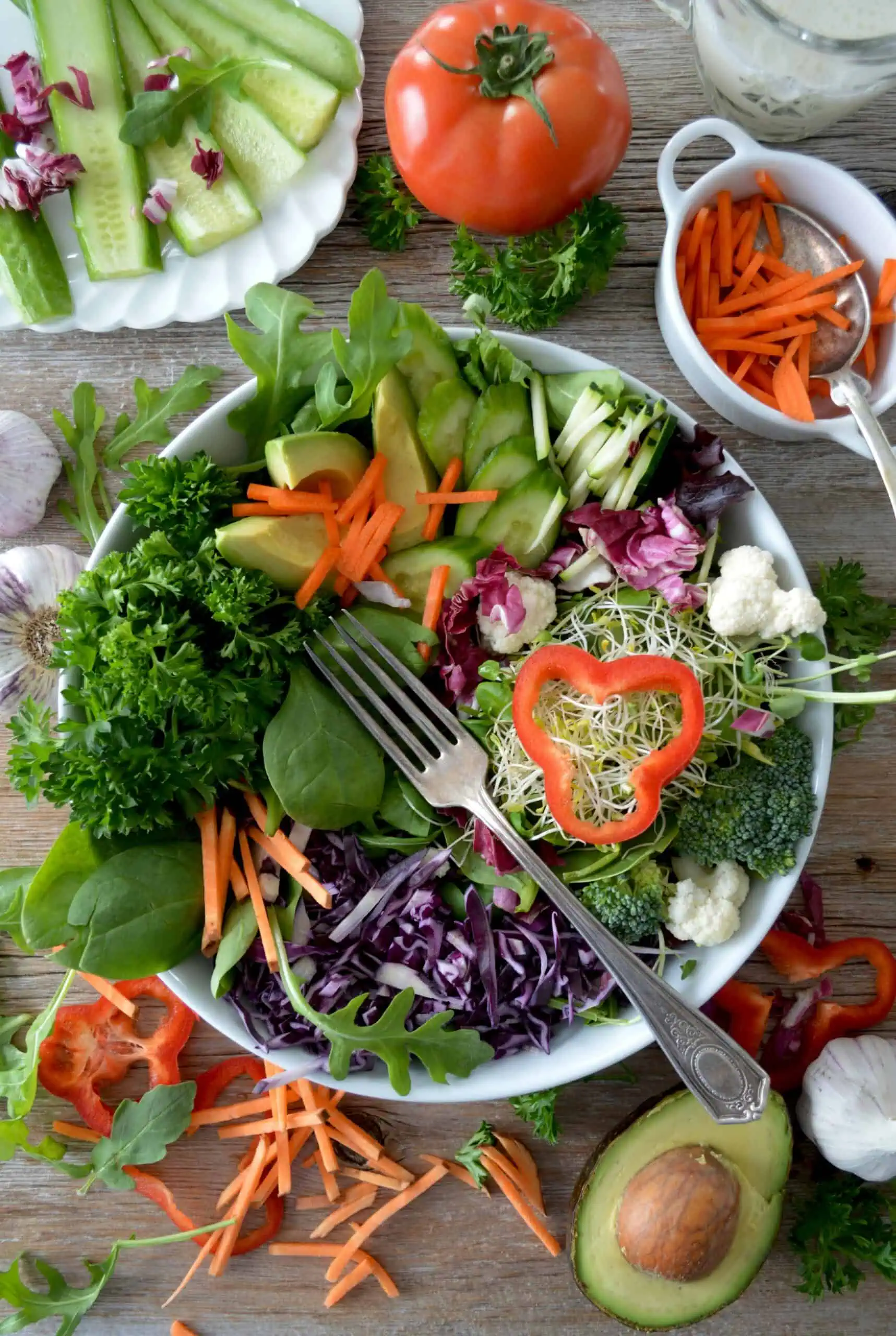

Too Many Low FODMAP Vegetables?
Yes, you can have too many low-FODMAP vegetables in a serving. So it’s important to understand the portion size that is low in these fermentable sugars. Also, vegetables still contain fibre and can be more challenging for those with IBS if consumed in high quantities. A good guide is to aim for five servings of vegetables a day; one serving equals ½ cup cooked or 1 cup raw. I recommend having a maximum of two servings of low-FODMAP vegetables at one time.

Bottom Line:
Low FODMAP vegetables include a variety of produce such as carrots, bean sprouts, eggplant, kale, spinach, arugula, tomato, zucchini and cucumber. Using an App, like Monash Low FODMAP app, can help in determining the appropriate serving size that is considered Low FODMAP. Remember this science-based, digestion diet helps relieve symptoms of bloating, pain, gas and changes in bowels (i.e. diarrhea or constipation). Additionally, it’s recommended that a FODMAP-trained Registered Dietitian assist you through the three stages, from elimination to reintroduction and personalization.

We hope you enjoyed this blog on Low FODMAP vegetables and found it helpful on your digestive journey. Our dietitian team is happy to support you with the Low FODMAP diet virtually or in person. Let us know what your favourite Low FODMAP vegetables are as well!