Vitamin D Foods
You’ve probably heard about vitamin D or the ‘sunshine vitamin’ – that it’s essential for our health and vitality. However, less attention is drawn to vitamin D foods. Which foods are the highest, and how much do we get? Additionally, can we get enough vitamin D in our diets, or do we need supplements? This blog intends to ‘shed light’ on vitamin D and to ensure you’re getting enough.

What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin also known as the ‘sunshine vitamin’ because we make it when our skin is exposed to sunlight. However, in Canada, due to our latitude being too far north, our skin is unable to synthesize vitamin D during the fall and winter months easily. Also, wearing sunscreen blocks the UVB rays but helps to protect us from skin cancer. Thus, we may need to incorporate vitamin D-rich foods or supplements into our diet to meet our needs, especially during the fall and winter months.

In light of the current global pandemic, vitamin D is gaining attention for potentially decreasing the risk of coronavirus. However, these are mostly observational studies that show lower vitamin D levels are associated with a greater risk of COVID-19 infection and perhaps even greater improvement in outcomes for black people with higher levels, according to a new study published in JAMA Open Network. However, cause and effect are still being studied in more rigorous studies. Nevertheless, vitamin D appears to play a potentially significant role and could be a compelling reason to ensure we are getting enough from vitamin D-rich foods and/or supplements.
Did you know? Vitamin D appears to potentially play a role in COVID-19 infection and could be a great reason to ensure we’re getting enough from vitamin D foods and/or supplements.
Why Is Vitamin D Important?
- Builds strong bones. Vitamin D supports the absorption of calcium and phosphorus — two minerals that are essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Low levels of vitamin D increase the risk for Osteoporosis and rickets.

- Supports immune functioning. There are vitamin D cells on your immune cells.
- Potential Health Benefits: Low levels have been linked to cancer and muscle weakness. Additionally, vitamin D may lessen depression, but needs more research before the causal relationship is determined.

Did you know? It’s possible to boost your mood with food! Read 3 Ways to Boost Your Mood with Food
- Disease Prevention: Research is continuing to investigate the role of vitamin D in the prevention of heart disease, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and reducing the risk of Multiple Sclerosis (2017,2006).

What’s the Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the most common nutrient deficiencies in the world. According to Statistics Canada,one in three Canadians are below the optimal blood level of vitamin D (50 nmol/L) for healthy bones. Interestingly, only 34% of Canadians took a vitamin D supplement, but of those 85% were above the cut-off compared to 59% of the non-supplement users.
Higher Risk for Vitamin D Deficiency?
- Those over 65 years– Kidneys cannot convert vitamin D to its active form as readily. Plus, skin changes to convert less efficiently into active form of vitamin D and with less time spent outdoors.

- Skin Colour-Darker skin colours have more melanin, which helps protect the skin against excess sunlight as a natural sunscreen. This means that individuals with darker skin are at a higher risk for vitamin D deficiency because they need to spend longer periods in sun because of the lower absorption.
- Overweight or Obese–Vitamin D is extracted from the blood and absorbed by fat cells. The more fat cells, the more vitamin D is pulled from the blood. Thus, the risk of deficiency is increased.
- Breastfed Infants–Breastmilk doesn’t provide enough vitamin D and babies have limited sun exposure.
- Certain medical conditions such as Crohn’s disease, cystic fibrosis, celiac disease decrease the intestines’ ability to absorb vitamin D foods or supplements.

How Much Vitamin D Do We Need?
This can be a difficult question since there are several factors that will increase your risk for vitamin D deficiency (see those mentioned above). Consequently, these may increase your supplement requirements to achieve adequate vitamin D levels. Your age, your race, where you live, how much time spent outdoors, the time of day you’re outside, sunscreen usage, amount of clothing and health conditions will all impact your vitamin D status.

What’s the Optimal Vitamin D Level?
Vitamin D blood levels considered optimal range widely from as low as 30 ng/mL or 50 ng/mL to 75 or 100 ng/mL. Importantly, keep in mind that it takes around 3 months of supplementing to achieve higher vitamin D blood levels. Additionally, these markers are not routinely tested in bloodwork and could be an additional fee.

Vitamin D Supplements
Canadian Cancer Society recommends adults take a daily supplement of 1,000 IU of vitamin D3. However, many individuals require high amounts of supplementation. Currently, 4,000 IU is the safe upper limit for vitamin D supplementation, according to the Institute of Medicine (IOM). Be sure to speak with your dietitian if uncertain about the amount of supplementation that is right for you.

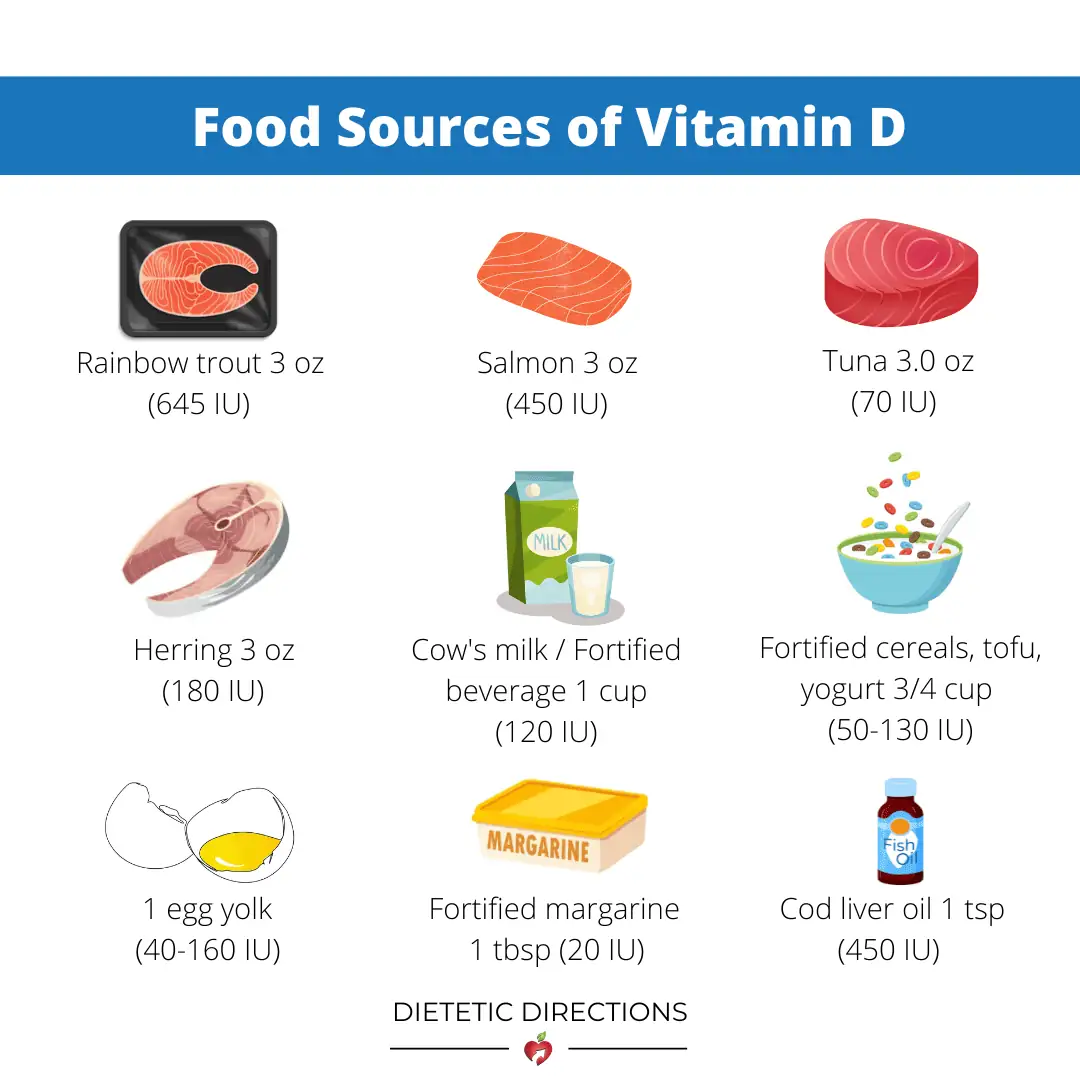
What are Foods with Vitamin D?
| Food | Serving Size | Vitamin D (IU) |
| Rainbow Trout | 3 oz (85 gram) | 645 |
| Salmon | 3 oz (85 gram) | 450 |
| Cod Liver Oil | 1 tsp | 450 |
| Herring | 3 oz (85 gram) | 180 |
| Fortified Cereals, tofu, yogurt | ~3/4 cup | 50-130 |
| Cow’s Milk or fortified beverage | 1 cup | 100 |
| Tuna | 3 oz (85 gram) | 70 |
| Egg Yolk (higher if chicken is outdoors or fed vitamin D enriched feed) | 1 egg | 40 -160 + |
| Fortified Margarine | 1 tbsp | 20 |
Can We Get Enough Vitamin D in Foods?
Theoretically, we could get enough vitamin D from foods and sunshine to meet our requirements. However, this would involve monitoring how much you are consuming to ensure you’re meeting requirements based on your age and risk factors. Therefore, getting enough vitamin D from diet alone can be challenging.
As a dietitian, I believe the best bet is to ensure you are getting a vitamin D3 supplement to meet your requirements and enjoy time in the sun with sunscreen. It’s also a great idea to enjoy vitamin D foods as part of your healthy diet since many of these options contain lots of great nutrition.

Bottom Line:
Vitamin D is vital for optimal health and disease prevention. Unfortunately, deficiency of vitamin D is quite common and needs to be corrected through adequate supplementation, vitamin D foods and potentially time outdoors.Finally, vitamin D foods include options like rainbow trout, salmon, cod liver oil, fortified cereals, milk and eggs.

Speak with a dietitian (see one on our team) to ensure you’re meeting your vitamin D requirements. If you are concerned your vitamin D levels are too low, ask your doctor to check your blood levels.

Now’s your turn! Did you know which vitamin D foods were the best sources? Do you include these options in your diet?