Breastfeeding Nutrition Basics
Breastfeeding nutrition is key for providing both baby and momma with nourishment during a crucial time for growth, development, and, of course, bonding. As a first-time mom, I found those early days were filled with a surplus of information, sleep deprivation, as well as a BIG learning curve on how to actually breastfeed. Nevertheless, today in celebration of Breastfeeding Awareness Month, let’s review the breastfeeding nutrition basics. First, I will highlight the nutritional benefits, then 3 key (and often overlooked) breastfeeding nutrients and lastly, I’ll share a chart for lactating mothers with takeaways.
This post was sponsored by the Egg Farmers of Ontario, as always, all opinions are genuine.
Today’s blog is a follow-up to my pregnancy nutrition blog where I explored key nutrients vital during that phase. Also, as a foodie dietitian, I will again be providing meal examples and breaking down meal prep solutions so they realistically fit into a busy lifestyle. For more on Meal Planning, check out our blog on How to Start Meal Planning along with a FREE resource on How to Meal Plan Like a PRO (I wrote the content myself and it’s available in English and French).

Grab your FREE & comprehensive, Meal Plan like a Pro! E-book. Order paper copies or PDF versions.
My Breastfeeding Journey
I heard that breastfeeding was challenging. I also had the clear message that it’s okay if it’s not for you or if it doesn’t work out. Because I was aware of the nutritional, economic and convenient benefits, I was eager to try my darndest to breastfeed. My biggest challenges included: pain with latching, uncertainty about amount of milk my baby consumed, nursing fatigue along with the worst back/neck pain from the hours AND hours dedicated to this specific, sedentary activity. Thankfully, my doctor’s office had an excellent lactation consultant (LC) for one-on-one support and troubleshooting. This was a game-changer for us and helped me gain confidence and skills to eventually get to pain-free nursing. Undoubtedly, if you’re struggling or a newbie, I would recommend seeking support of a LC before and after baby arrives. This support truly helped me to persevere and eventually love breastfeeding.
Andrea, Dietitian, shares her top nutrition tips for fellow breastfeeding mommas!
Breastfeeding Nutrition Chart for Lactating Mothers:
Breastfeeding Benefits for Baby Include:
- Boosts baby’s immune system with antibodies to fight infection.
- Offers the perfect nutrition – the right amount of fat, sugar, water, protein and vitamins for your baby’s development.
- Provides easy digestion for your baby’s small tummy and intestines.
- Promotes healthy infant weight gain.
- Supports bonding and contentment for both parties with hormonal production of oxytocin and prolactin during skin-to-skin contact.
- Studies show that breastfed infants may have reduced risk of asthma, allergies, obesity and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
What are Breastfeeding Benefits for Mom?
- Lowers risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
- Reduces risk of cardiovascular disease, type two diabetes, and high blood pressure.
- Lowers mom’s risk of postpartum depression and supports infant bonding.
- Helps with recovery from childbirth since oxytocin produced helps uterus return to normal size.
- Generally promotes faster weight loss after birth.
- Makes feeding convenient (no heating milk or filling bottles); you just need nursing bras or nursing tops to accessibly feed if out and about.
- Is cost-effective, as opposed to formula, which can be up to $10 a day depending on the brand, type and amount baby drinks.
In addition to benefits to the baby, breastfeeding benefits the mom too!
How Long is Breastfeeding Recommended?
Health Canada, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the World Health Organization all recommend exclusive breastfeeding for about the first 6 months, with continued breastfeeding along with introducing appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years of age or longer.
3 Key Nutrients for Breastfeeding Nutrition:
1. Choline
Many do not know that mom’s nutrition needs for choline increase while she’s pregnant (450 mg daily) and increase even further when breastfeeding (550 mg daily)! This increased choline requirement is due to mom’s supply being transmitted in milk as well. Therefore, a breastfeeding mom needs extra dietary choline to meet the demands of both baby and her body. Importantly, prenatal vitamins contain little to no choline, which underscores the importance of getting enough in the diet.
Pepper Ring Eggs are a tasty way for boosting choline intake while breastfeeding.
DYK: Choline requirements increase while pregnant and increase even further when breastfeeding. This essential nutrient supports mom’s health and infant’s development.
Are Pregnant & Breastfeeding Women Getting Enough Choline?
Research shows that ~90% of Americans (including pregnant and lactating women) are not meeting their adequate intake of choline. Similarly, the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans identify choline as an underconsumed nutrient. Therefore, this underscores the importance of boosting choline intake while breastfeeding for healthy blood cells as well as brain and neurological development. However, the good news is that eating choline rich foods helps to increase the choline in breast milk.
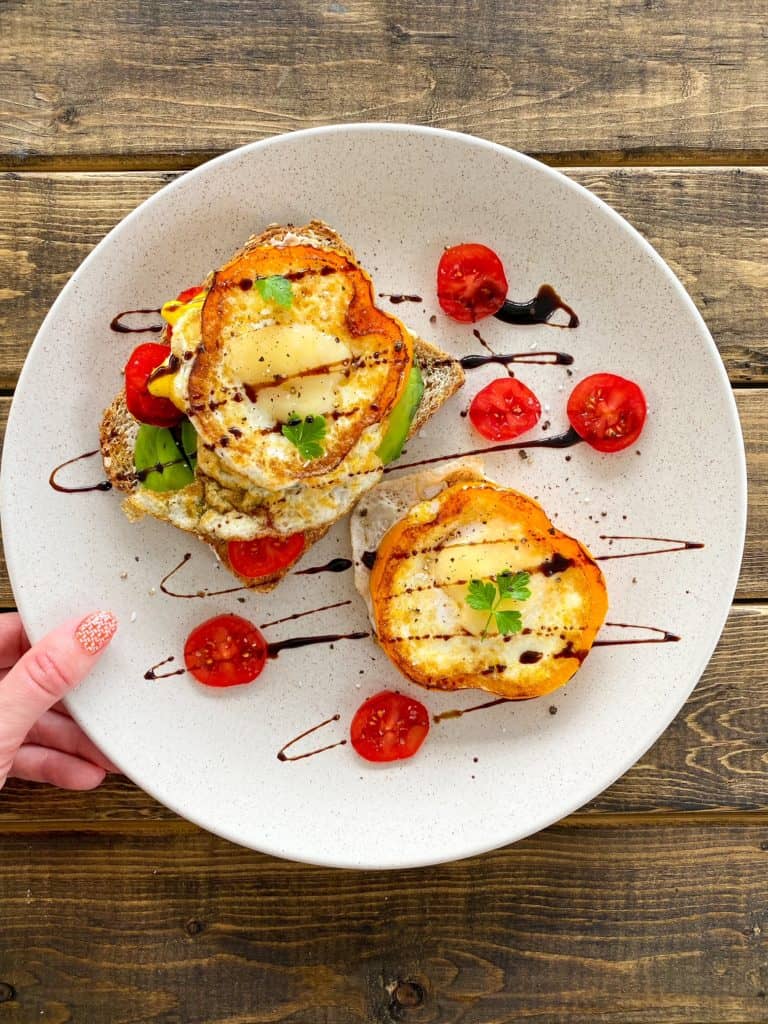
Prenatal supplements typically contain little if any choline (typically only 0–55 mg). Best bet is to get choline in your diet, like with our Avocado Toast with Eggs!
Why is Choline Important for Breastfeeding Nutrition?
- Firstly, choline is deemed an essential nutrient, which means our body cannot synthesize enough to meet our needs so we must consume through foods (or supplements).
- Involved in boosting maternal and offspring immune functioning.
- Supports intestinal health and is critical for the absorption of fat for lactation.
- Choline is vital in brain development and researchers have shown that it can positively influence infant memory.
- Supports tissue and eye development as well as muscle control.
- Boosts liver health along with healthy blood cells that carry oxygen.
- Inadequate choline intake has been associated with fatty liver since choline plays a role in transporting and lowering LDL or “bad” cholesterol. Specifically, choline is required to synthesize very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles, which transport fat from the liver.
- Acts as a precursor for a neurotransmitter that help muscles contract and plays a role in memory, attention and mood. These effects can have long-term impacts on children.
- Research shows that choline supplementation during pregnancy and lactation reduces inflammation in breastfeeding women postpartum.
DYK: Choline is an essential nutrient that is often underconsumed. It’s also important for transporting cholesterol away from the liver, which helps improve fatty liver.
What’s a Top Dietary Source of Choline?
Eggs are a top and (personally) preferred dietary source of choline! Luckily, two eggs contain 12 grams of protein and ~70% of a pregnant woman’s daily choline requirement and 55% of a nursing mother’s. However, remember not to skip the yolk since this contains most of the nutrition (including choline) and half the protein. To learn more about heart health and debunking the cholesterol myth check out our blog, Ways to Boost Heart Health.
Avocado Egg Plate recipe is a simply elegant meal that’s great for breastfeeding nutrition too!
Why are Eggs Nutritious?
Eggs contain 14 essential nutrients like lutein, selenium and vitamin A, which all support a healthy pregnancy, are important while breastfeeding and for general body functioning. Interestingly, eggs are super fresh and go from farm to grocery store in 4 to 7 days in Ontario. Additionally, they’re a cost-effective protein that leads to many quick and easy meals. Be sure to check out our Cheap, Healthy meals blog for more meal ideas.
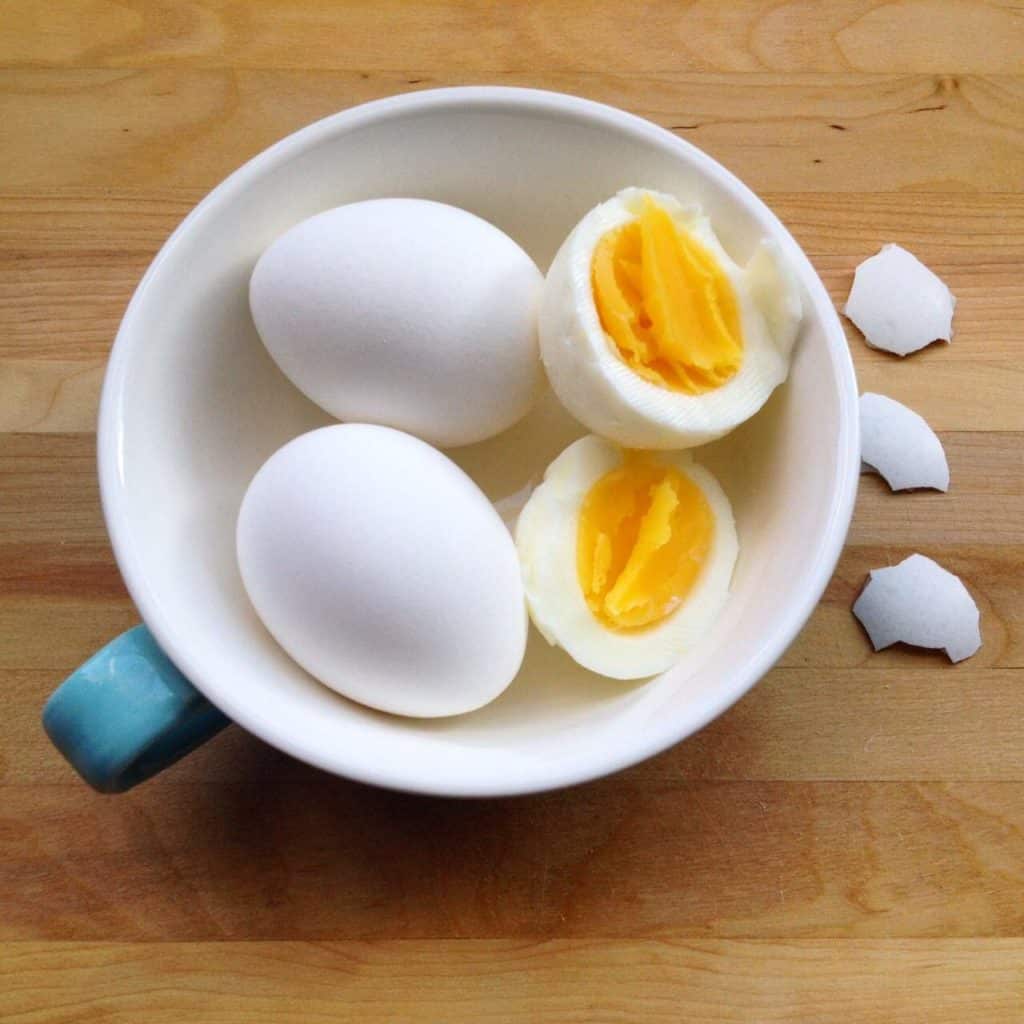

Eggs contain 14 essential nutrients and support healthy pregnancy, breastfeeding and body functioning.
Food Sources of Choline:
- Eggs
- Liver
- Meat & Seafood
- Dairy Products
- Soybeans, soy milk and tofu
- Beans
- Quinoa
- Brussels sprouts
- Cruciferous vegetables
- Green peas
- Shitake mushrooms
Are you uncertain if you’re meeting your choline requirements? Speak with a Registered Dietitian.
Choline Boosting Tips:
- Consume choline-rich foods such as: eggs, beef, chicken, fish, milk and soy products.
- Meal prep choline-rich foods for added convenience. For example, hard-cook eggs, batch BBQ meats or fish and steam edamame for a snack or added to a stir-fry.
- Speak with a Registered Dietitian if uncertain you’re getting enough choline (especially if at higher risk for inadequacy with pregnancy and breastfeeding, or as a vegetarian or vegan).
- Prep mini egg muffins for freezer or breakfasts-to-go.
- Finally, speak with a Registered Dietitian before taking a choline supplement to ensure appropriate dosing for your needs.
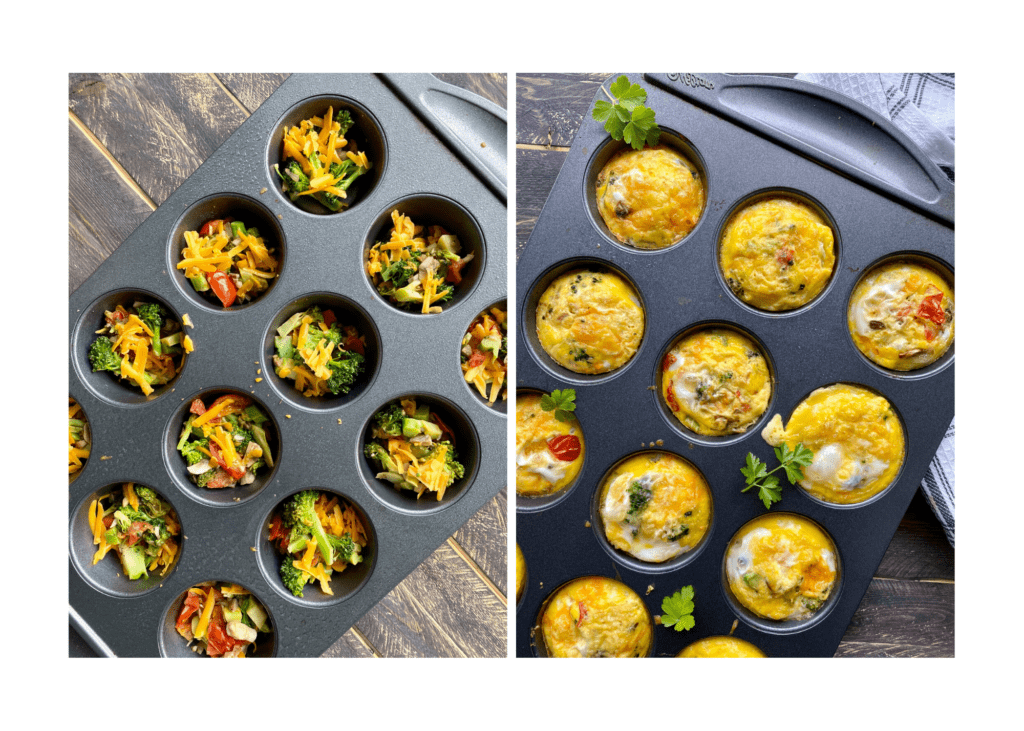
Try our mini egg muffins for a simple make-ahead breakfast that boosts choline and protein intake!
Choline-Rich Recipe Ideas



2. Omega-3’s for Breastfeeding Nutrition
Omega 3’s are heart-healthy, anti-inflammatory fats crucial during breastfeeding for baby’s brain and eye development as well as mom’s mood (by decreasing risk for postpartum depression.) Mothers with higher omega-3 intake have higher amounts in their breast milk as well, which can be beneficial for baby. Additionally, omega-3’s even support baby’s immunity. So choosing fatty fish is an excellent way to boost omega-3 intake (especially DHA and EPA), but there are also supplements, which can be discussed with your dietitian.
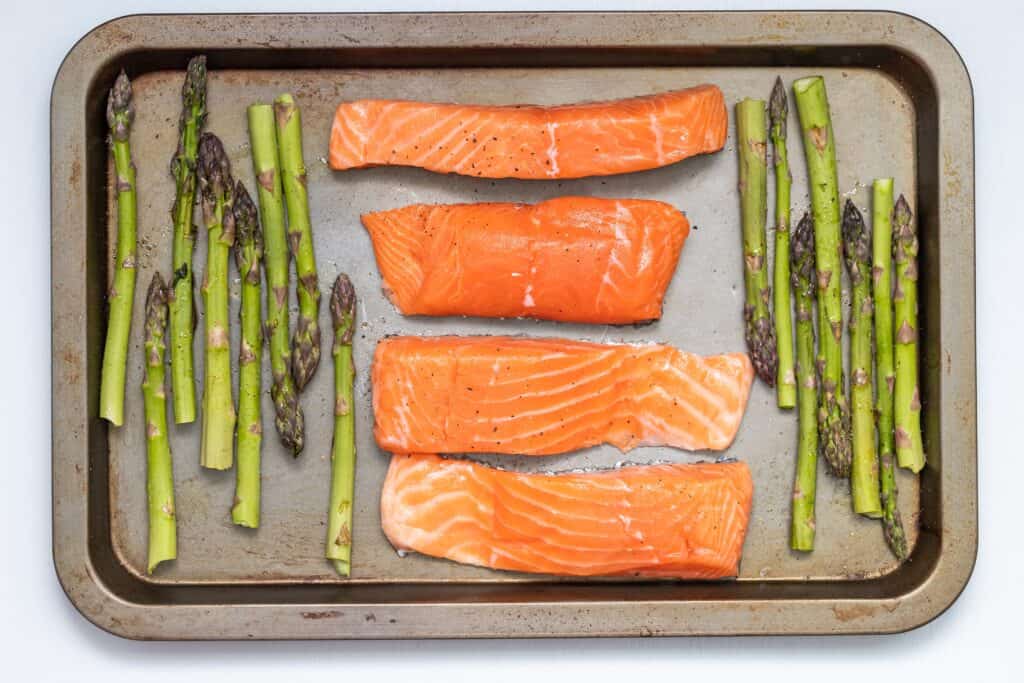
Salmon is an example of fatty fish which helps to boost omega-3 intake!
DYK: A baby’s brain grows the fastest in the last trimester of pregnancy and the first two years after birth. This is why Omega-3’s (specifically EPA and DHA) are vital!
Omega-3 Recommendations:
Guidelines from the World Health Organization (WHO) recommend that those pregnant and breastfeeding consume an average of 300 mg per day of DHA, either from fish or taking a supplement. Similarly, the 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans states that those pregnant or breastfeeding should consume 8–12 ounces of seafood per week. This includes choosing varieties that are higher in EPA and DHA and lower in mercury such as salmon, herring, sardines, and trout. This equates to consuming fish two to three times a week, which would yield approximately 200-500 mg of EPA and DHA per day or 1,400-3,500 mg per week.
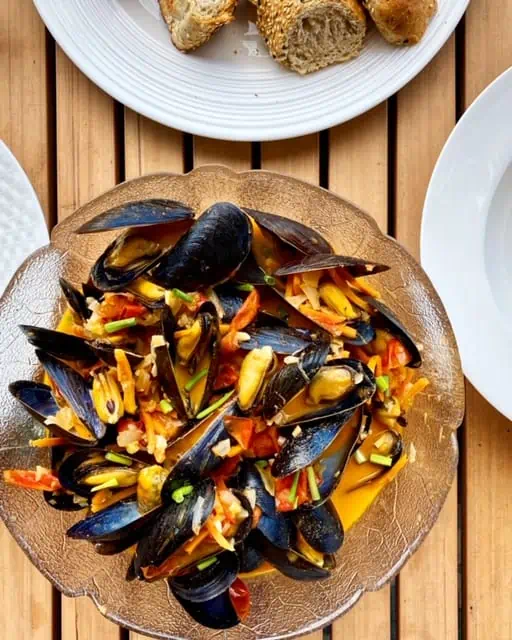
Our Coconut Red Curry Mussels are a great way to boost your seafood intake while breastfeeding.
Salmon provides high-quality protein along with other nutrients like vitamin B12 and vitamin D, which supports bones and teeth. A 3-ounce (palm-sized) serving of salmon contains around 2,000 mg of omega-3 (EPA & DHA) fatty acids.
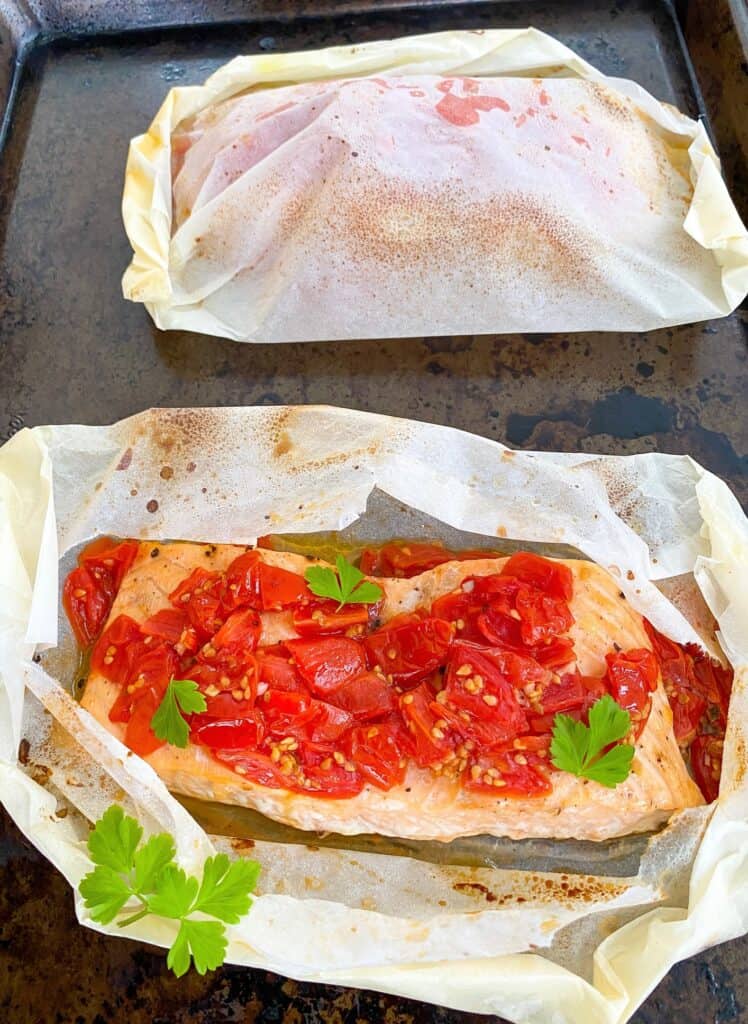

Bruschetta Parchment Salmon is both delicious and nutritious!
Why are Omega-3’s Important for Breastfeeding Nutrition?
- Omega-3’s are deemed “essential fatty acids” since our body cannot produce them and they must be consumed in food or supplements.
- The fatty acid DHA supports brain and eye development. (Note: DHA and EPA are the most biologically available, active forms, which come mainly from marine sources like fish and algae).
- Lowers triglycerides (fats in your blood) and blood pressure.
- May improve mild-to-moderate post-partum depression.
- Supports infant and maternal immunity.
- Specifically DHA works synergistically with choline (mentioned above for importance during pregnancy and lactation) for supporting baby’s memory, cognition and brain health.
- Supplementing mom with omega-3’s during breastfeeding appears to potentially help children perform better on sustained attention tasks at 5 years of age compared to non-supplementing mothers.
- Finally, if mom doesn’t have sufficient omega-3’s in diet, baby will deplete mom’s stores to support brain growth and development.
DYK: Prenatal supplements typically contain no omega-3’s. Speak with a Dietitian to meet your needs!
Omega-3 Boosting Tips for Breastfeeding Nutrition:
- Keep salmon handy in the freezer or in pantry in cans. This allows you to whip up a sandwich, wrap, use as a salad topper or sauté a fillet for dinner.
- Enjoy omega-3-rich fish ideally two to three times a week.
- Try new types of fish like bluefish, bass and flounder and experiment with different cooking methods.
- Try a homemade salmon poke bowl!
- Utilize a meal theme to encourage consumption – like “Fish Friday” or Taco Tuesday with Salmon or Rainbow trout fish tacos.
- Use canned salmon to make “salmon salad” filling to add in wraps, sandwiches or on crackers for a meal.
- Add anchovies or sardines to tomato sauce or as a pizza topping.
- Pan-fry fish for a 10-minute protein source to add to your meal.
- Grill fish on BBQ.
- Enjoy sushi with omega-3 rich fish. Spicy salmon rolls are a fave!
- Steam mussels for a nutritious option with omega-3 fats.
- Avoid tilefish, swordfish, shark and king mackerel since they contain high levels of mercury.


Omega-3-Boosting Recipe Ideas:
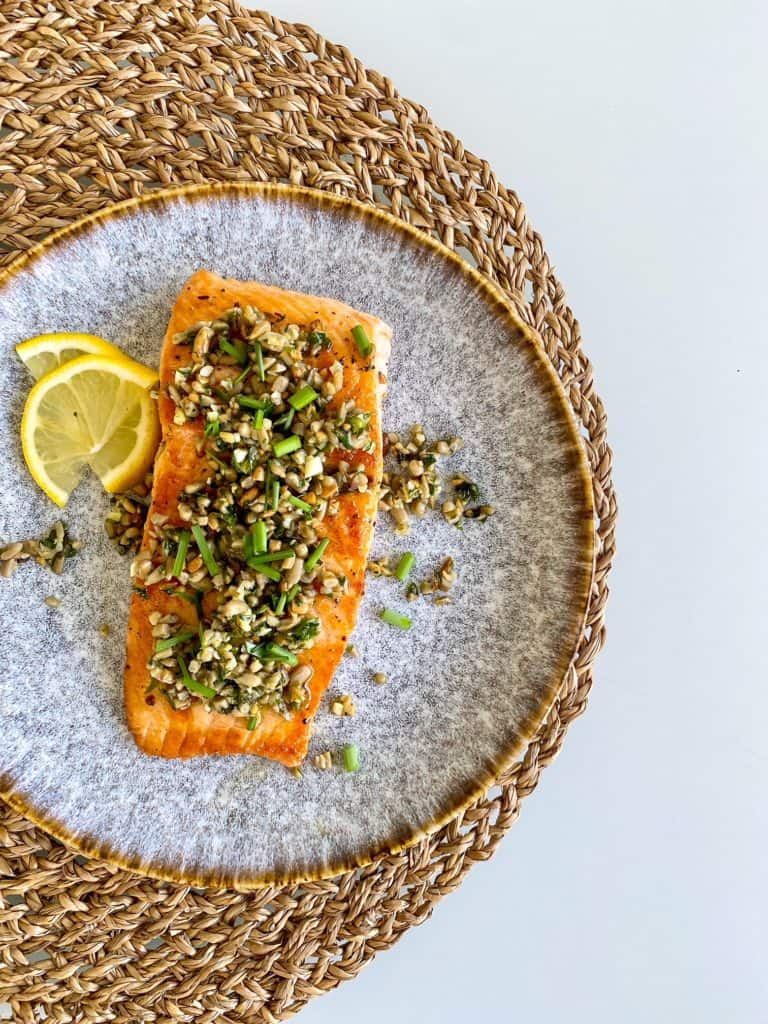



3. Iron for Breastfeeding Nutrition
A newborn received most of their iron stores when they were in the womb. Therefore, the necessity of iron during pregnancy was KEY for both mom and baby’s health! However, baby’s birth iron stores only last for four to six months, at which point breast milk alone is insufficient to meet baby’s iron requirements. This is where baby’s first foods come in to boost their dietary iron intake (but that’s another blog!) Nevertheless, during breastfeeding nutrition (or supplementation) it is still vital to prevent low iron levels. Additionally, I typically recommend mothers request iron levels assessed post-pregnancy to determine if their vitamin regime needs to include iron supplementation (speak with a dietitian for one-on-one counselling).
Iron is essential to the baby and mom and can be obtained through diet and/or supplementation.
DYK: Iron is the only nutrient deficiency that is significantly prevalent in both developed and developing countries.
World Health Organization
What are Iron Requirements?
The dietary recommended intake of iron for breastfeeding mothers is 9 mg daily. This is significantly lower than 30 mg recommended when pregnant or 18 mg for women 19-50 years old. The lower intake is because breast milk is not a high source of iron and therefore does not take much iron from mom. Nevertheless, if your iron level is low (or you are anemic) your needs may be higher to correct a deficiency. Importantly, iron deficiency postpartum is not caused by breastfeeding but is likely pre-existing from pregnancy or childbirth blood loss.
Why is Iron Important for Breastfeeding Nutrition?
- Iron is used by the body to make red blood cells (haemoglobin) which transport oxygen throughout the body.
- Plays an important role in brain development and children’s cognitive abilities.
- Maternal anemia or low iron can cause fatigue, low milk supply and decreased mood associated with postpartum depression. (Be sure to have your doctor check your iron levels if uncertain if your level is low and requires treatment.)
- Helps maintain healthy skin, hair and nails.
- If you had good iron stores when pregnant, your baby would have received more iron as well.
Dietitians can help you work towards meeting dietary requirements. Speak with us today!
Dietitian TIP: Request iron status to be monitored while pregnant and postpartum. Speak with a Registered Dietitian about iron supplementation if food intake isn’t correcting a deficiency.
What are Risk Factors for Low Iron?
- Maternal history of iron deficiency.
- Significant blood loss during childbirth.
- Return of a period within the first six months.
- Pre-term infants or low birth weight babies have lower iron stores.
- Digestive issues causing malabsorption of iron (such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis).
- High intake of antacids (which can prevent your body from absorbing iron).
- High level of exercise like running, which increases body’s iron demands.
Interested in adjusting your diet to improve iron deficiency? Consider booking an appointment with a registered dietitian for one-on-one advice.
Breastfeeding Nutrition Iron-Boosting Tips:
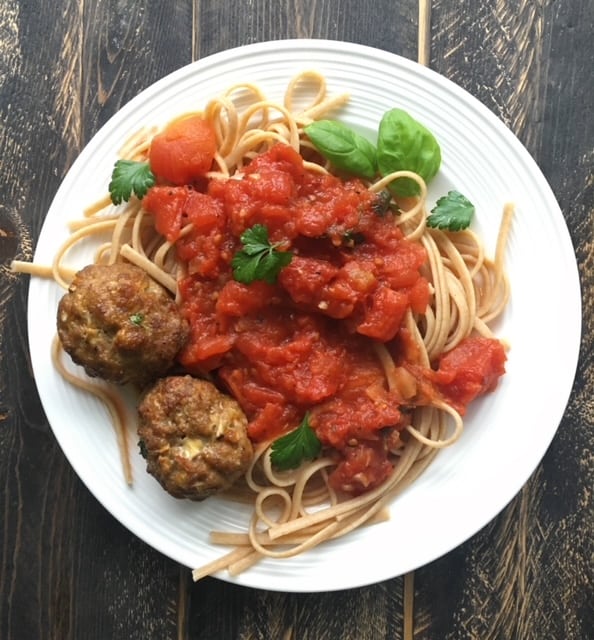
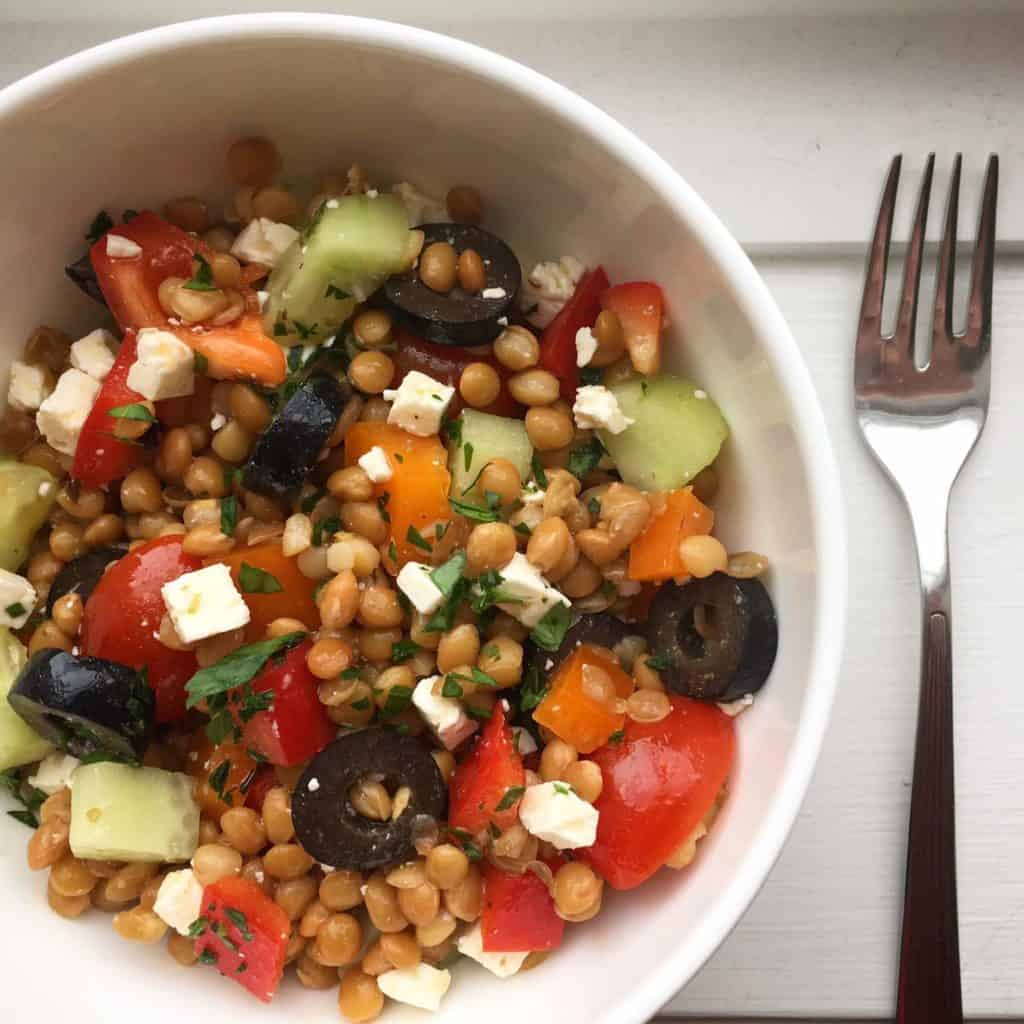
- Emphasize iron-rich foods such as red meat, liver, legumes, fortified grains, eggs, tofu and leafy greens.
- Pair iron-rich foods with vitamin C to enhance the absorption of non-heme iron. In fact, a research study found that adding 63 mg of vitamin C to a grain-based, non-heme iron-rich meal boosted iron absorption by almost 300%.
Garlic Lentil Bruschetta uses tomatoes (vitamin C) to enhance iron absorption in the lentils.
- Have your iron level checked by doctor and consider supplementing to correct low levels. Speak with a dietitian for dosing and advice on choosing right supplement to prevent constipation or stomach pain.
- Continue taking iron supplements if you have a history of iron deficiency anemia.

Iron-Boosting Recipe Ideas:



How Many Extra Calories to Eat When Breastfeeding?
Yes, you will need approximately 200 to 400 extra calories daily while breastfeeding. You might find your appetite has kicked up a notch. I know mine did! This is because breastfeeding requires energy for continued milk production. Therefore, including an extra snack (or two) of nutrient-rich foods is recommended. Remember that we don’t need to overdo it with extra calories, but we want to honour our hunger as our body has increased nutritional demands when nursing our baby.
Grab our FREE Snack Guide! This includes power combos to keep you feeling fuller for longer.
How Much Hydration Do I Need?
Importantly, you’ll need to increase your water/hydration while breastfeeding to keep your milk supply. After all, breastfeeding every two to four hours is dehydrating. Aim for 10 to 16 cups of water, which can come from hydrating foods, water and beverages. However, emphasize nutrition-rich options as opposed to empty calories like sugary drinks or alcoholic beverages. Additionally, limit caffeine to 2-3 cups daily or 200-300 mg caffeine. To help with increasing your hydration, keep water bottles with you on the go, have one at your nursing chair and add water to meals and snacks.
Remember to drink water to hydrate and satisfy your thirst while breastfeeding.
Will the foods I eat impact the taste of my breast milk?
Yes, your dietary choices will flavour your breast milk and expose your baby to different tastes. Be sure to vary your diet so your baby experiences a variety of tastes which can help with acceptance of new foods when this upcoming stage begins.
Many babies enjoy garlic-flavoured milk!
Bottom Line for Breastfeeding Nutrition:
Breastfeeding nutrition is a special opportunity to nourish your baby. However, it also comes with challenges and competing demands. If breastfeeding is not possible for you, please do not blame yourself and know that formula can be an excellent nutritional substitute. Overall, take care of yourself physically and mentally. Additionally, choose foods that are rich in choline, omega-3 fats and iron. Be sure to save our diet chart for lactating mothers for key reminders. Finally, continue to emphasize unprocessed foods like fruits and veggies, whole grains, legumes and protein-rich options. Remember when you make healthy choices, you and your baby will reap the rewards.
Now it’s your turn. What are your favourite foods to include when maximizing your breastfeeding nutrition? How do you ensure you’re getting enough of the key nutrients?